In the next article we are going to take a look at Cockpit. This open source project will offer us a friendly, web-based administrative interface for servers. Its interface has been developed by Red Hat and Fedora developers, although we will also find it officially available for Ubuntu and Debian.
Cockpit interacts directly with the operating system from a real Gnu / Linux session, all from a web browser, with an easy-to-use interface. From this interface we will be able to administer our server and perform tasks with a mouse click. With this software, sysadmins will be well helped to perform simple administration tasks, manage storage, configure network, inspect logs, etc.
General characteristics of Cockpit
- We can manage services; start, stop, restart, reload, disable, enable, mask, etc..
- We will also be able to manage user accounts; add users, delete them, block them, assign them the administrator role, set the password, force the password change, etc..
- It will give us the opportunity to manage the firewall.
- Container management Cockpit.
- We will be able to perform the policy management SELinux.
- Launcher settings iSCSI.
- We can also configure the server VPN OpenConnect and the NFS client.
- We can perform actions such as shutting down or restarting the system.
- Diagnose network problems.
- Hardware device management.
- System updates for hosts dnf, yum, apt.
- Users we can write our own modules to connect them to Cockpit.
- Cockpit is for use completely free and available under the GNU LGPL.
These are just some of the Cockpit features. They can consult all of them in detail from the project website.
Install Cockpit on Ubuntu 20.04
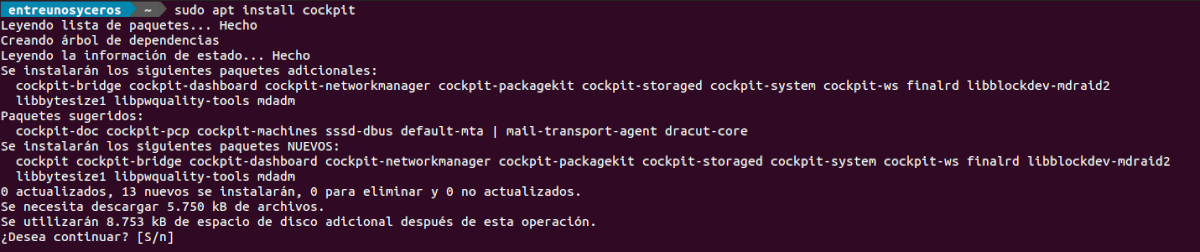
Cockpit is available in the official Ubuntu repositories. Installation is as simple as running the following set of commands in a terminal (Ctrl + Alt + T):
sudo apt update; sudo apt install cockpit
Access to the Cockpit web interface
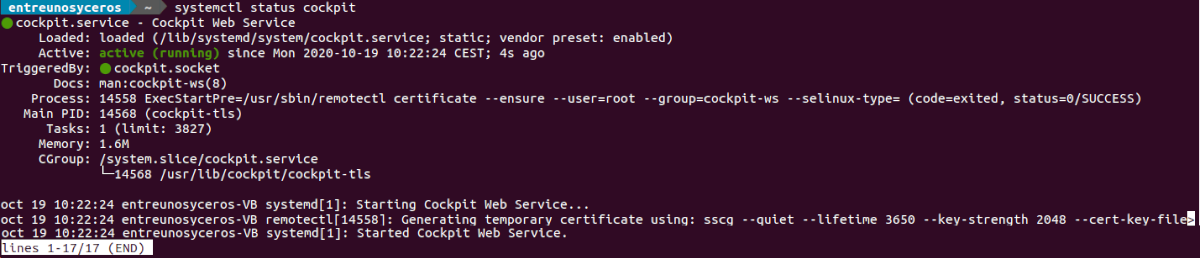
Service Cockpit should start automatically after installation. We can confirm that the service is running using the following command in a terminal (Ctrl + Alt + T):
systemctl status cockpit
If the service is not running, we can start it by executing this other command:
sudo systemctl start cockpit
Service Cockpit uses port 9090. To access its web interface, all you have to do is open our web browser and go to the address:
http://[IP-SERVIDOR/Nombre-de-host]:9090
If you have a UFW firewall service running, enable port 9090 with the command:
sudo ufw allow 9090
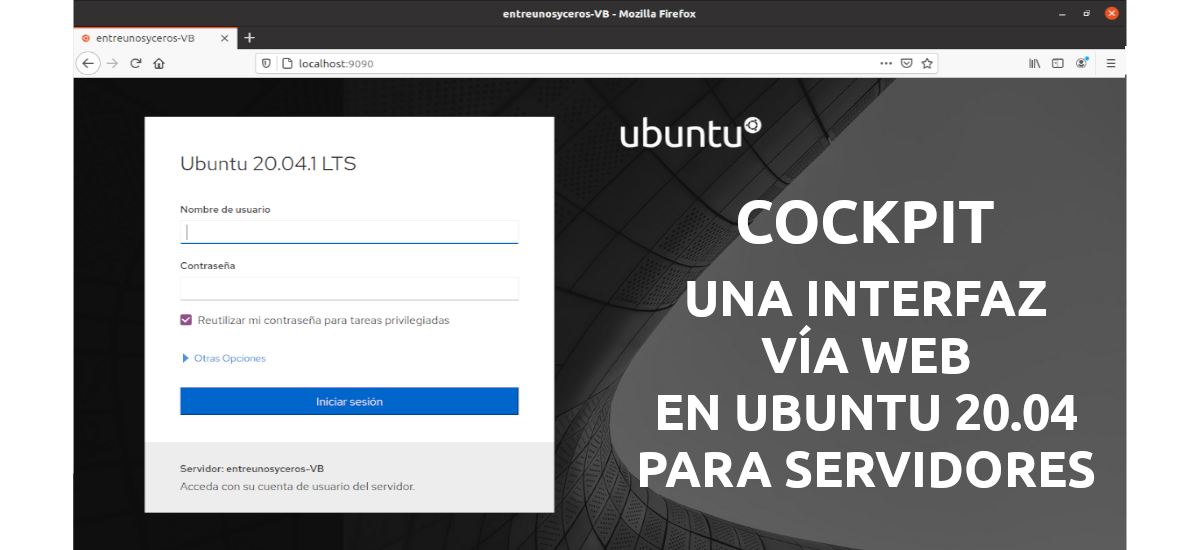
The web interface
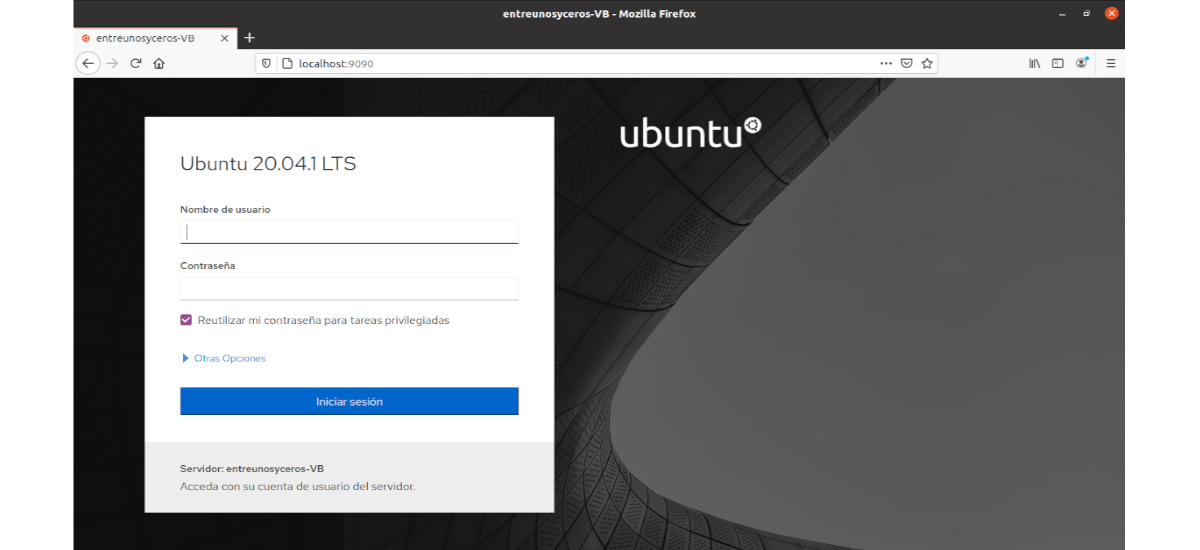
Once installed, we can access its interface by typing in the web browser https: // localhost: 9090 (or the hostname / IP where we have the program installed). Use any of your system's user credentials to log in. When we access the interface, we can see the following sections:
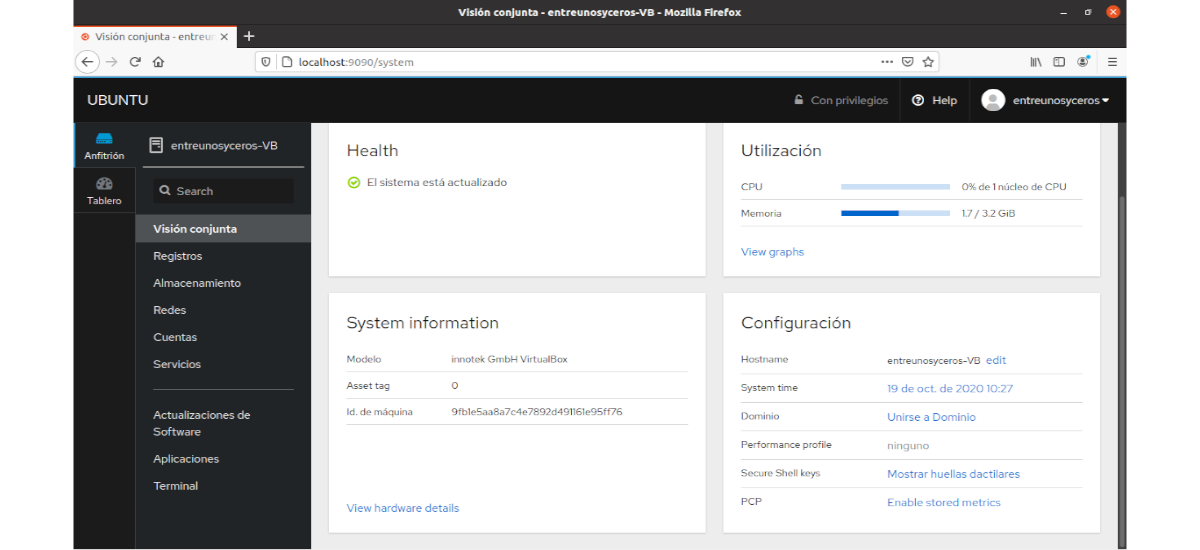
Joint vision
The Cockpit System Overview Screen It will show us the details of our server, CPU, memory, disk and about the configuration.
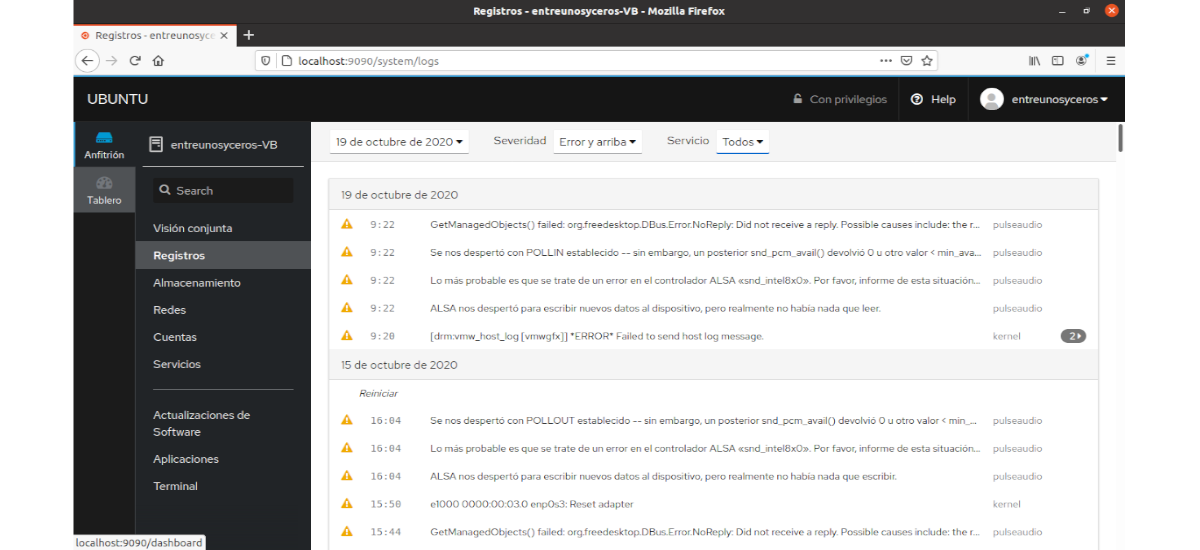
Records!
The Records section shows the user the list of errors, warnings and other important log details of our server.
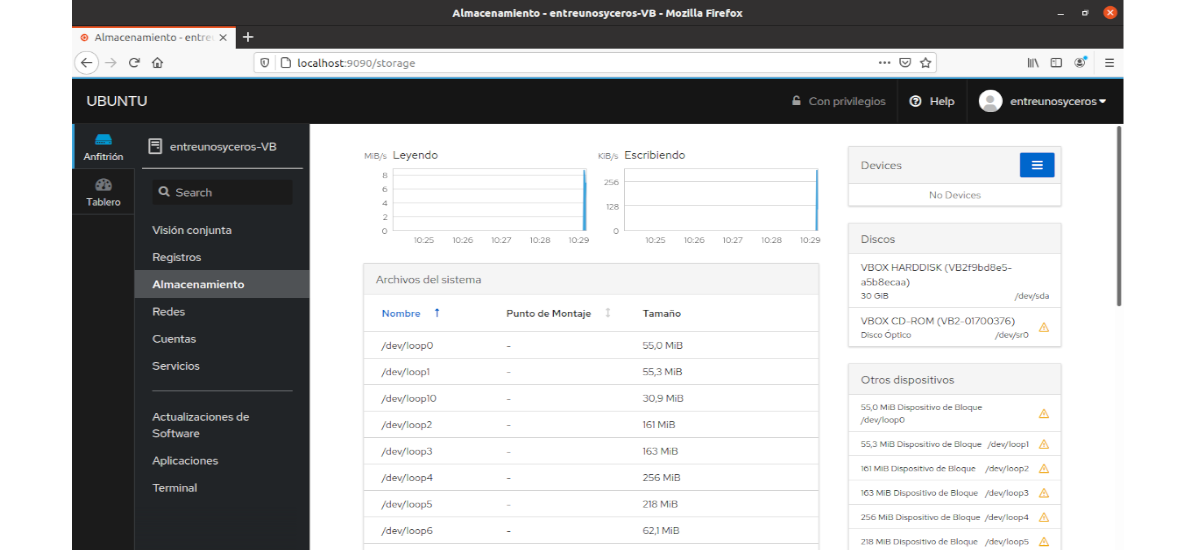
Storage
This section shows the system hard drive read and write details.
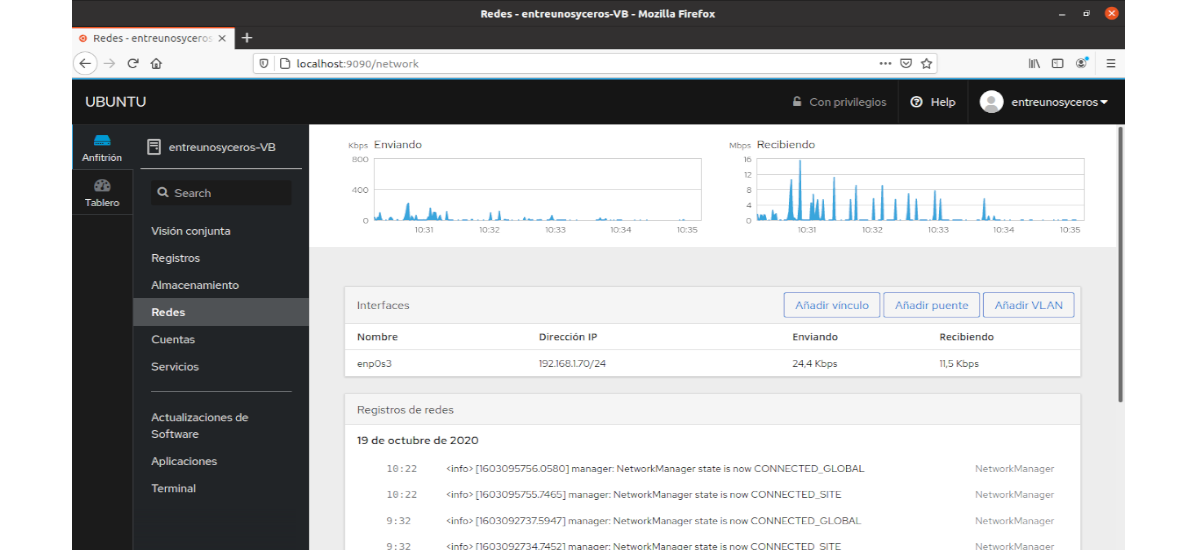
Industrial
In this section we can view network logs, incoming and outgoing traffic from the network interface card.
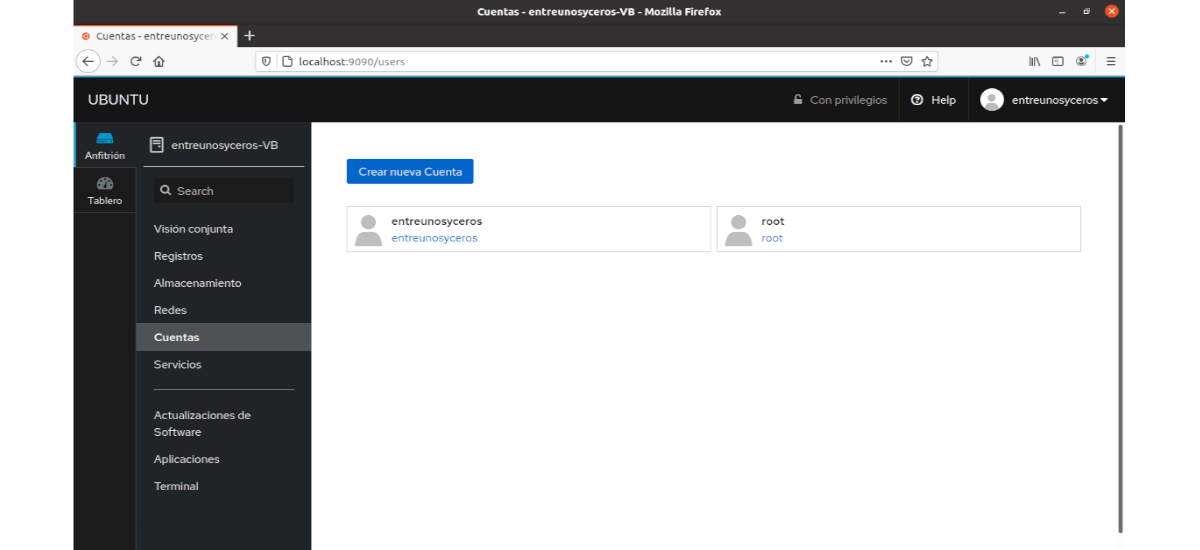
Accounts
Here we can create new users, delete existing users and change the user's password.
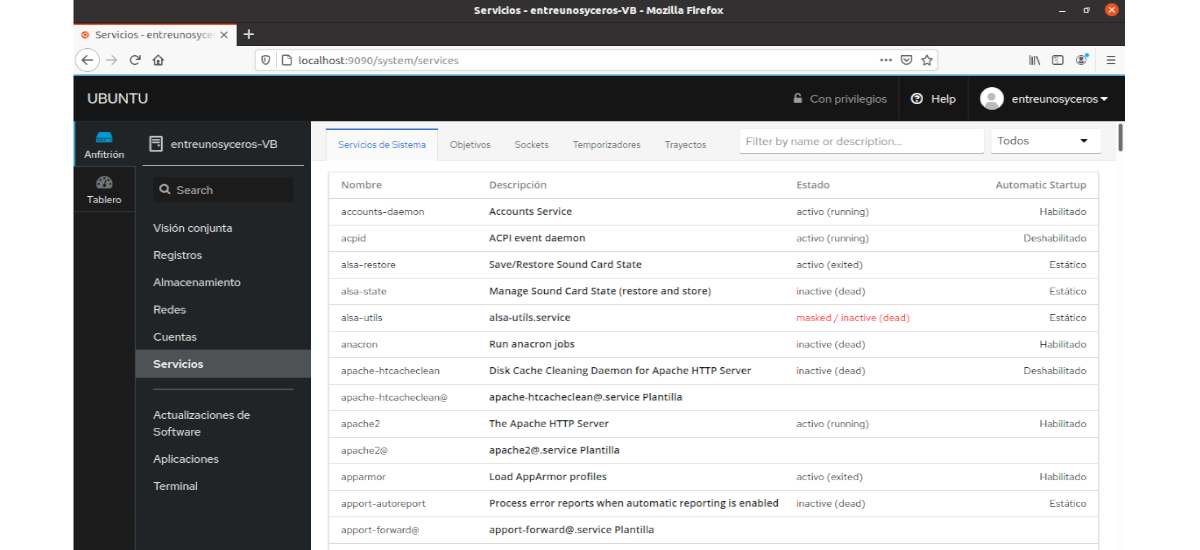
Services
This section shows the list of active, inactive and failed services.
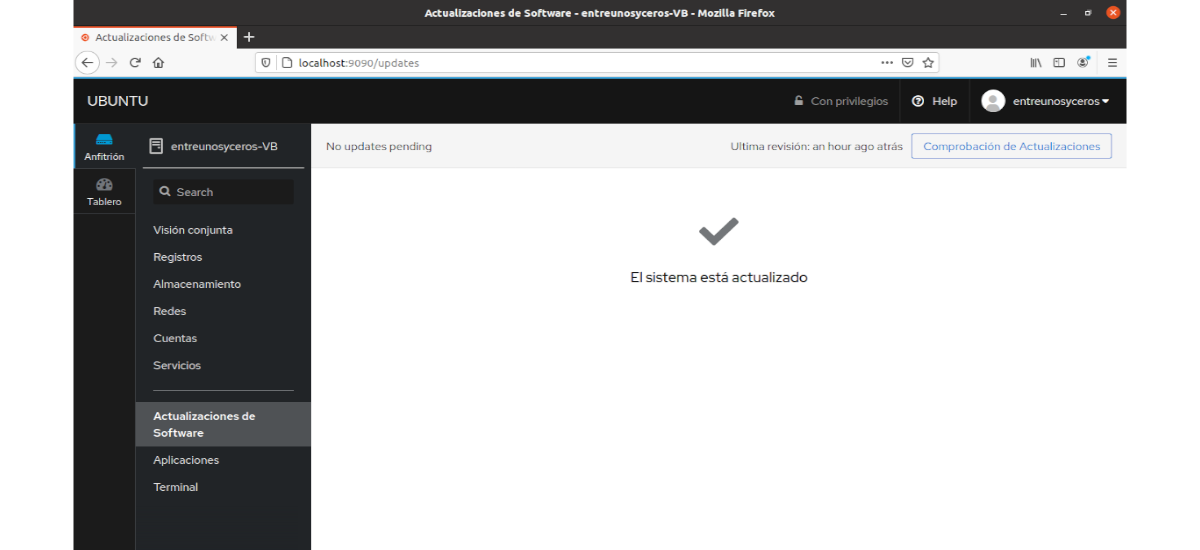
Software updates
Here we will have the possibility of check and update the system.
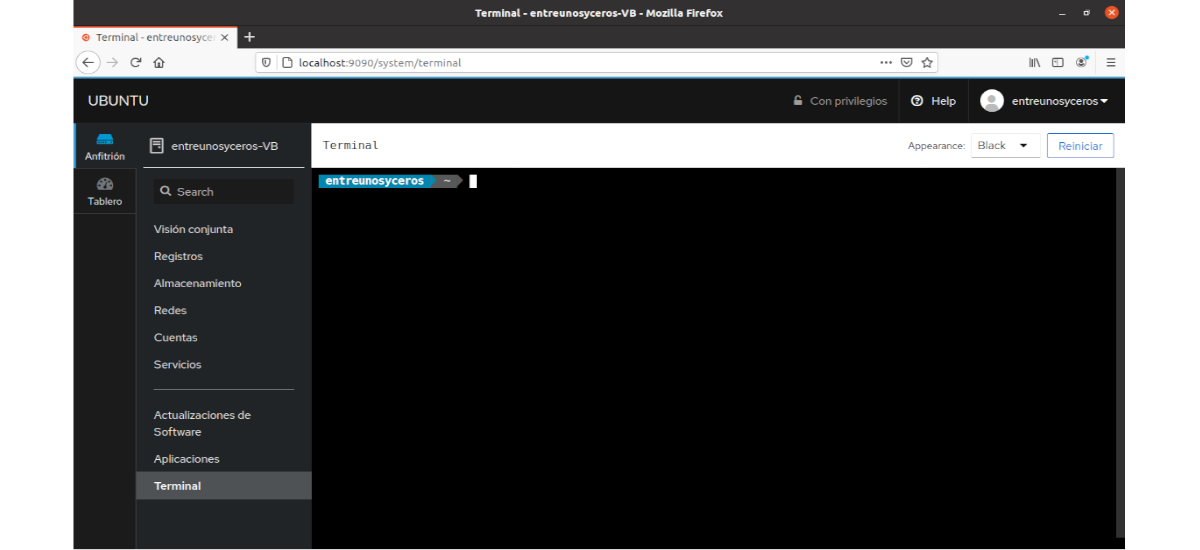
Port
Cockpit has a built-in terminal. This will allow us to execute command line operations without problems. You will not need SSH for your server or install any remote communication tool. We will be able to perform all the command line operations that we could do in the normal terminal window of our system.
Uninstall Cockpit
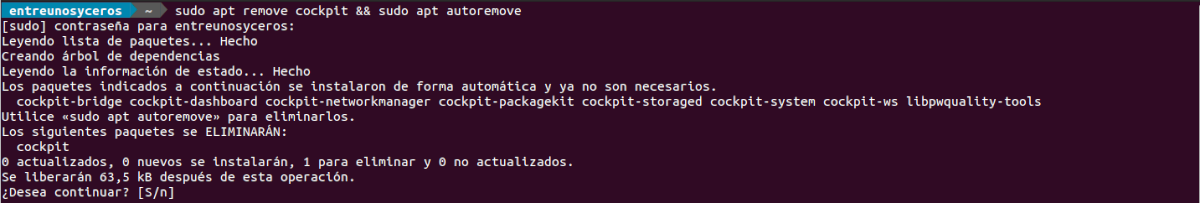
For remove this tool from our operating system, we will open a terminal (Ctrl + Alt + T) and we will only have to write in it:
sudo apt remove cockpit && sudo apt autoremove
This is a good option for budding administrators. The installation is quite simple and has a direct use. If we have a network full of remote systems, adding them to the Cockpit panel can be easily managed.
To learn more about this project, any user can find more data in his web page or documentation of the project.