
Defrag partitions in Linux: How is it done and why?
Continuing the exploration of more basic and essential commands of the GNU/Linux operating system, today we will address the command "e4defrag".
This command is provided by the package “e2fsprogs”, and its function is to allow users the power "defragment partitions in linux".

Basic Commands for Linux Newbies: 2023 – Part One
But, before starting this post on how "Defragment partitions in Linux", we recommend that you then explore the previous related post:


Defragment partitions in Linux: Anything useful?
What is defragmenting a hard drive or disk partition?
In a simple and understandable way, we can describe the defragment a hard drive or disk partition as the process of rearranging fragmented files on a disk or partition so that they are together and in order.
This is because, in most operating systems (especially Windows), when a file is saved to a disk or partition, it is often save in multiple chunks. Which means, the file can be divided into different areas of the disk instead of being in a single block.
And it is precisely the disk defragmentation process, which helps to keep all the parts of a file in a single block, achieving optimization of disk performance, by making access to files faster and more efficient, thus improving the processing speed of the computer.
Is it recommended or necessary to defragment a disk/partition in Linux?
On GNU/Linux operating systems, this will largely depend on the file system being used. Since, in general, modern file systems like “Ext4, Btrfs, JFS, ZFS, XFS, or ReiserFS” handle the file fragmentation process more effectively than Windows “FAT/NTFS”, and what older Linux filesystems such as "Ext3".
Therefore, defragmentation may not be as necessary on modern file systems. However, on older file systems or in cases where there is a high amount of file write and delete activity, defragmentation may be recommended, even for modern file systems.
So that, running a defragmentation in very sporadic or specific cases will always be a good thing, and never something bad; regardless of the operating system used, the file system implemented or the type of disk used. And in any case, it will always be something important, the keep regular monitoring of hard drive health to make sure it is working optimally.
How to defragment partitions in Linux?
First, we must make sure that we have the package “e2fsprogs” installed using the CLI or GUI package manager of our GNU/Linux Distro used. Once this is done, we only have to do the following to:
View the defragmentation level of a disk/partition/folder
sudo e4defrag -c /disco/partición/carpeta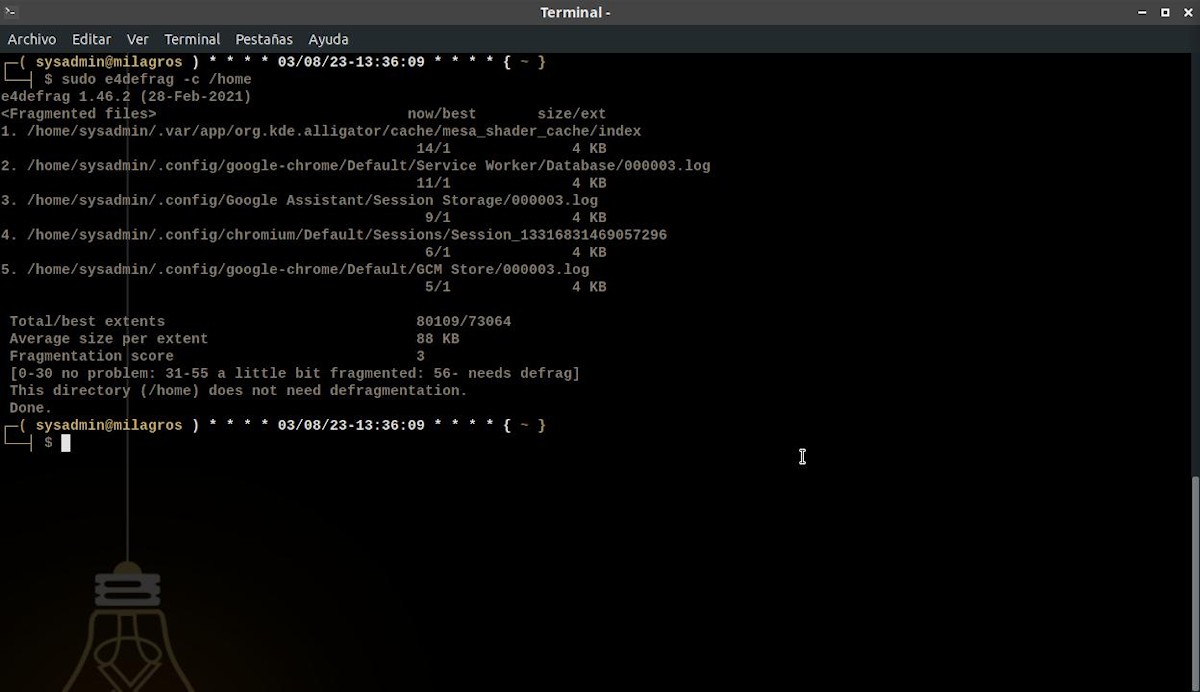
Note: Executing this command results in a fragmentation score. If it reaches a score below 30, it is advisable not to take any action. Whereas, between 30 and 60 indicates that it is advisable to run a defrag soon; and between 61 and 100 indicates that it is urgent to proceed with the defragmentation.
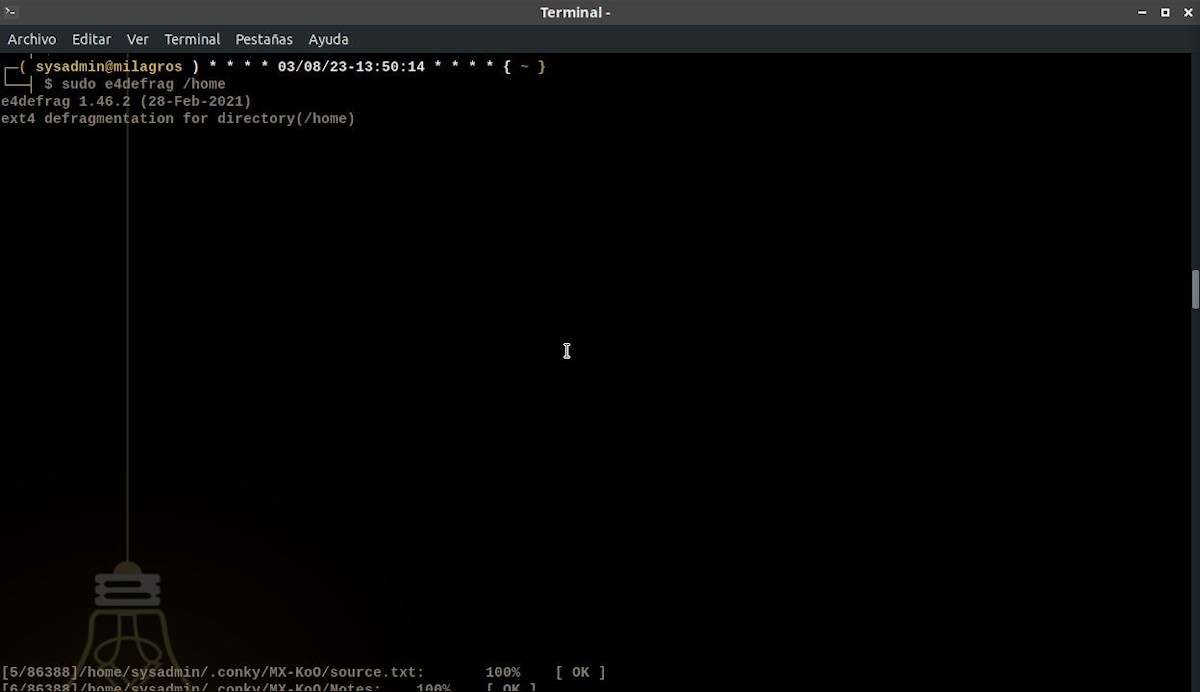
Run defragmentation of a disk/partition/folder
sudo e4defrag /disco/partición/carpetaAs seen in the following screenshot:


Summary
In short, we hope that the e4defrag command used for "defragment partitions in linux" allow many to implement it at the right time and the appropriate conditions.
Finally, remember to share this useful information with others, in addition to visiting the home of our «site» to learn more current content, and join our official channel of Telegram to explore more news, tutorials and Linux updates. West group, for more information on today's topic.

Interesting, I had no idea that it could be defragmented in GNU/Linux, perhaps it never made me curious, but since I have /HOME on HDD, this information seemed excellent to me.
Regards, Carlos. Thanks for your comment. We are very glad that the information has been interesting to you, and perhaps useful in the future.