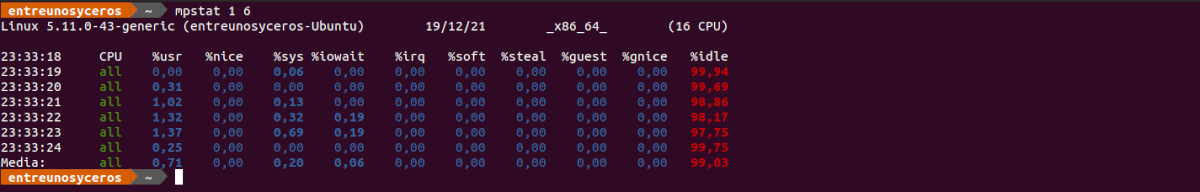
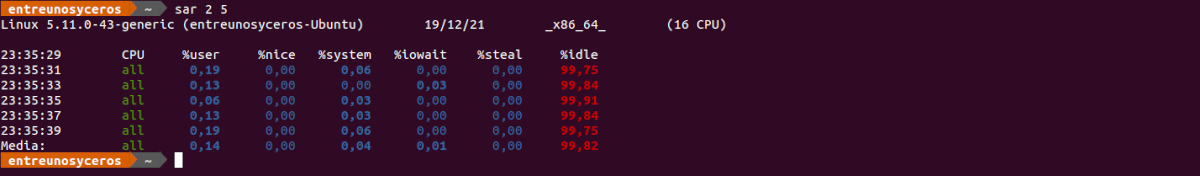
In the next article we are going to take a look at SysStat. This is a collection of tools with which we can monitor our system, which is also open source and free. With these tools we can debug performance problems in Gnu / Linux systems, it will also allow us to see the performance data of the system in real time, or analyze the data of the files that these tools can generate.
Its installation is quite simple. In the following lines we will see step by step how to perform the installing this toolkit on Ubuntu 20.04. The installation instructions can also be followed on other versions of Ubuntu and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
Sysstat General Features
- You can show us the average statistical values at the end of the reports.
- You have the possibility of detect new devices on the fly (disks, network interfaces, etc ...) that are created or recorded dynamically.
- UP and SMP machine compatibility, including machines with multi-core or hyper-processing processors.
- Support for Hotplug CPUs (automatically detects processors that are disabled or enabled on the fly) Y Tickless CPUs.
- Works on 32-bit or 64-bit architectures.
- Needs to too little CPU time to run.
- System statistics collected by sar / sadc can be saved to a file for future inspection. Allows you to configure the duration of the data history that will be kept. There is no limit to the duration of this history, but the space available on our storage device.
- System statistics collected by sar / sadc can be exported in several different formats (CSV, XML, JSON, SVG, etc ...).
- iostat can display statistics of managed devices.
- It has smart color output to facilitate the reading of statistics.
- Sysstat has translated into many different languages.
- Sysstat commands can automatically select the unit used to display sizes for easy readability.
- May generate graphics (SVG format) and display them in our favorite web browser.
- Sysstat is free / open source software and is available for free under the GNU General Public License, version 2.
- The latest version of Sysstat can always be found in the creator's website.
These are just some of the features of the program. They can consult all of them in detail from the project's GitHub repository.
Install SysStat on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
We can find this set of tools available in Ubuntu repositories. Therefore, the first thing we will have to do is update the software available from the repositories. We can do this by opening a terminal (Ctrl + Alt + T) and executing the commands in it:
sudo apt update; sudo apt upgrade
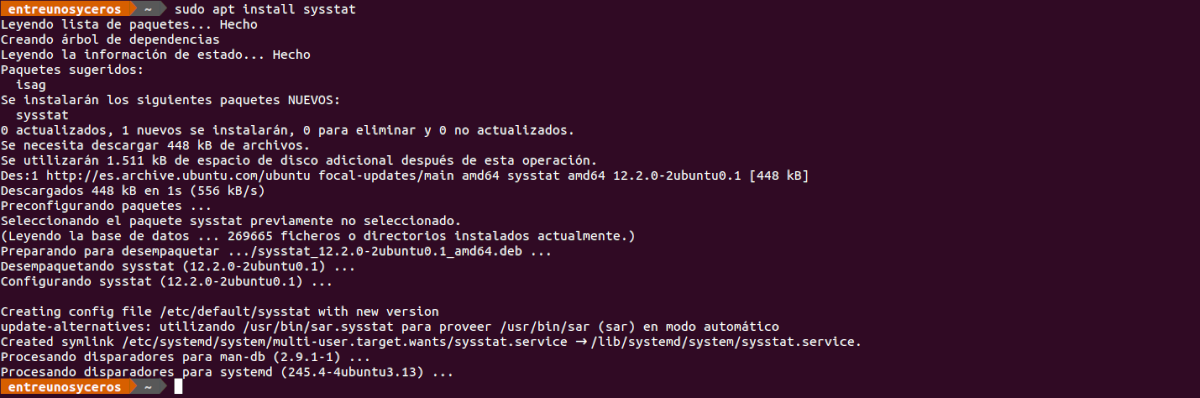
Then we can install SysStat in Ubuntu 20.04. As I was saying, this set of tools is available in the Ubuntu repositories, so we can use APT for the installation. It will only be necessary to write in the same terminal:
sudo apt install sysstat
After the installation, we will perform a minimum configuration necessary for SysStat to work correctly. By default, the supervision of this tool is disabled, so we will have to enable SysStat monitoring. We can do this by editing the following file:
sudo vim /etc/default/sysstat
Here we will only have to set ENABLED to true:
ENABLED="true"
The next step will be to save and close the file. Now only remains enable the SysStat service and start it by running:
sudo systemctl enable sysstat sudo systemctl start sysstat
When the service is started, we can use the utilities to monitor system performance and usage activity. What's more, Sysstat also contains tools that you can program via cron or systemd to collect and create a history on performance and activity data.. All these tools can be consulted in the documentation available from the project website.
uninstall
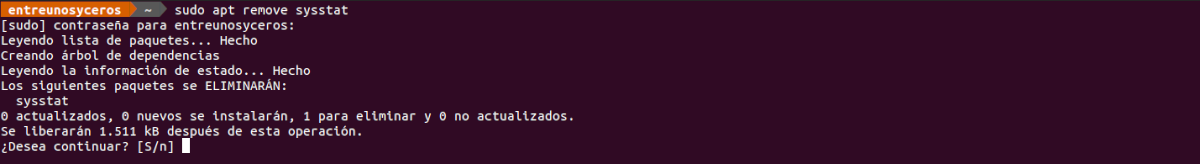
For remove this application from our system, it will only be necessary to open a terminal (Ctrl + Alt + T) and execute the command in it:
sudo apt remove sysstat
For help or useful information on the use of these tools, users can consult the information published in the GitHub repository or project website.