Yesterday we talked to you about security in Ubuntu, we were talking about antivirus on Gnu / Linux and how to use them as a security tool.
Well, I recognize that viruses are not the only threat that exists in the computer world and that many times the intrusions of other people in our system is more dangerous than a virus that writes I Love You on our screen. For this there is a very powerful tool that many people use and know the firewall or firewall.
But are there firewalls in Ubuntu?
All operating systems have firewalls, inasmuch as they are simple rules in charge of redirecting external information traffic to our operating system. So in Ubuntu Well installed by default for several versions already, I think I remember that it has been installed since version 7.04. And you will tell me that you have the latest version but you don't see any firewall. Well the explanation is simple, the firewall of Ubuntu It does not have a graphical interface and is only managed by console.
This initially turned out to be chaotic for many users, so in a short time there was a solution and a graphical interface was created for those users who wanted it. The firewall in Ubuntu is called Ufw, in case someone dares to use it in the terminal. And the graphical interface called Gufw, is included in the repositories of Ubuntu so you can install it through the terminal or through the Ubuntu Software CenterYou can even search for the package and download it as before.
Once installed handling is simple.
The first thing you have to unlock with the password root to be able to handle with him. Normally by default the wow it is deactivated so you will have to activate it.
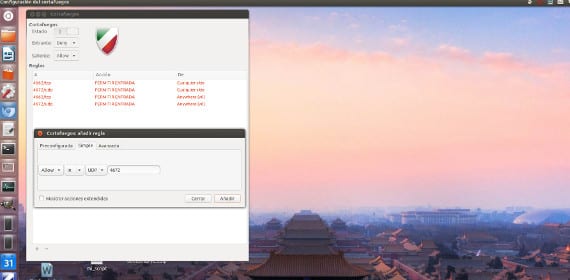
Once activated, the standard configuration is loaded that allows all the outputs of the computer to the Internet but no external input to the Internet, that is, you can safely navigate because they will not be able to operate the pc from the outside. You can also create rules in which you say which entries you allow and which exits. Normally the inputs and outputs are regulated by ports, there are many and each program uses a different one. Thus the emule or amule uses the 4662 and 4672 by default while the Ttransmission use a different port.
To create rules you just have to press the "+" sign and a window will appear with three little eyelashes to choose the rulemaking method.
From Simple, you can create rules for a default port. This allows you to create rules for services and applications that are not available in Preconfigured. To configure a range of ports, you can set them using the following syntax: NROPORT1: NROPORT2.
From Advanced, you can create more specific rules using the source and destination IP addresses and ports. There are four options available to define a rule: allow, deny, deny, and limit. Reject will return a message «ICMP: destination unreachable»To the applicant. Limit allows you to limit the number of unsuccessful connection attempts. This protects you against brute force attacks. Once the rule is added, it will appear in the main window of wow.
And so you will have configured and ready your firewall or firewall. A very important tool that you remember can turn against you, because if you do not remember the firewall or the ports that have been closed or opened, a multitude of problems can arise. You will tell me.
More information - Gufw 0.20.4 , Gufw, ClamTk virus cleanup in Ubuntu,
I've been trying to use it for months following all the indications they mention, not only in this article but in many others on the net, and I think that the only distribution that works correctly is in OpenSUSE, the rest in the others; it takes longer to activate and configure it than to stop working.
Hi 🙂 Gufw works perfectly on every Ubuntu version. Its releases are synchronized with each of the Ubuntu versions. A slaudo.
I want to configure gufw to deny all incoming and all outgoing traffic except for firefox, thunderbird, filezilla, update manager, ubuntu software centery jdownloader. unfortunately the list of automatic rules in the simple section is very short and does not include any of these programs. Can you write an article explaining how to find out what ports these programs use and how to get it?
Hello 🙂 Use the Listening Report to know which ports each program uses 😉 It is enabled in the Edit / Preferences menu.